AMD launched its AMD Epyc 8004 Siena processors, completing the 4th-gen Epyc family. The processors feature the Zen 4c core and cater to a range of applications, from the intelligent edge to data centers. They offer excellent energy efficiency for the intelligent edge, with up to 2× better performance per system watt compared to competitors. The chips provide balanced performance for space-constrained environments, and their core density and throughput savings benefit intelligent edge deployments. Additionally, OEMs like Dell Technologies, Lenovo, and Supermicro have unveiled systems leveraging the AMD Epyc 8004 series processors for various applications.
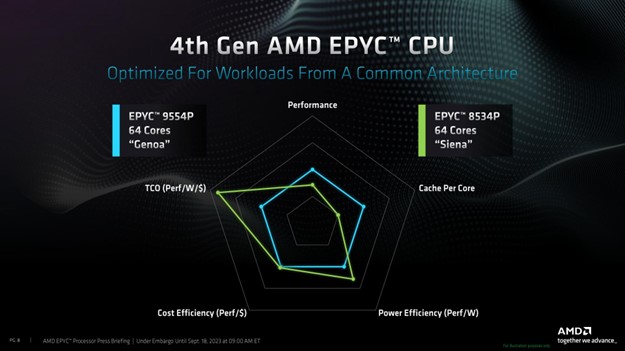
What do we think? The leading model in the Siena series is the Epyc 8534P, which boasts 64 Zen 4c cores distributed across 4 Zen 4c CCDs. In its default configuration, this part operates at a thermal design power (TDP) of 200W, with a configurable TDP (cTDP) range spanning from 115W to 225W. Essentially, it represents half of an Epyc Bergamo 9754, offering 50% fewer CPU cores, half the L3 cache, half the memory bandwidth, and, depending on the cTDP settings, approximately half the power consumption. These processors are tailored for customers prioritizing an abundance of CPU cores over peak single-threaded performance.
AMD releases Siena Epyc processors
AMD has introduced the AMD Epyc 8004 series processors, previously code-named Siena, marking the culmination of the 4th-gen Epyc lineup. These processors incorporate the specialized Zen 4c core architecture, enabling solution providers to build energy-efficient platforms suitable for a wide spectrum of applications, from the intelligent edge encompassing retail, manufacturing, and telecommunications, to traditional data centers hosting cloud services and storage solutions.
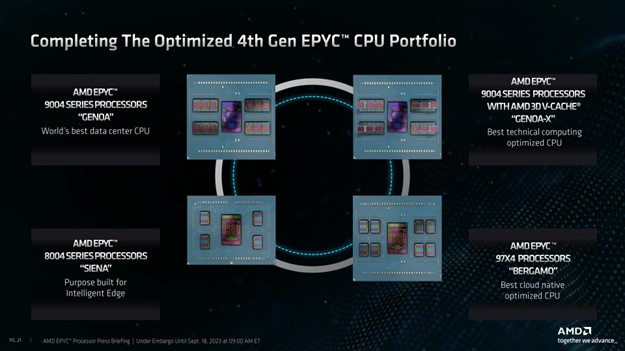
Notable features of the AMD Epyc 8004 series processors include:
- Versatile computing power: These processors are designed to cater to a broad spectrum of computing needs, spanning from the intelligent edge to conventional data centers.
- Enhanced energy efficiency: Leveraging the power-efficient Zen 4c core and the new SP6 socket, these processors offer remarkable energy efficiency. They can deliver up to twice the performance per system watt, compared to the leading networking models offered by competitors.
- Balanced performance: In industries where top-tier performance per watt is paramount, the AMD Epyc 8004 series processors strike a harmonious balance between performance and energy efficiency. For instance, in video encoding workloads, the Epyc 8534P model can achieve up to 2.4 times the aggregate frames per hour per system watt, compared to competing networking products.
- Optimized for the intelligent edge: Intelligent edge deployments, which often employ smaller server nodes rather than full racks found in traditional data centers, can greatly benefit from these processors. They enable substantial energy cost savings by offering improved core density and enhanced throughput.
For 1P servers in one-, three-, and 10-node configurations, Epyc 8534PN CPU-based servers use 34% less power and have 34% lower cost over the five years of this analysis.
The AMD Epyc solution supports an estimated 26 servers per one 8kW rack(s); the Intel solution supports 17 servers per one 8kW rack(s). AMD has 23% more cores and can deliver up to 11,414 units of integer performance per rack. Intel can provide up to 7,650 units of integer performance per rack.
| Model | Cores/Threads | Base/Boost Frequency (GHz) | L3 Cache (MB) | DDR Channels/ Max Memory Capacity | Max DDR5 Freq. (MHz) (1DPC) | PCIe 5 Lanes | Default TDP (W) | cTDP (W) | TCase Operating Range (°C) |
| 8534P | 64/128 | 2.3/3.1 | 128 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 200 | 155–225 | 0–75 |
| 8534PN | 64/128 | 2.0/3.1 | 128 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 175 | – | -5–85 |
| 8434P | 48/96 | 2.5/3.1 | 128 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 200 | 155–225 | 0–75 |
| 8434PN | 48/96 | 2.0/3.0 | 128 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 155 | – | -5–85 |
| 8324P | 32/64 | 2.65/3.0 | 128 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 180 | 155–225 | 0–75 |
| 8324PN | 32/64 | 2.05/3.0 | 128 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 130 | – | -5–85 |
| 8224P | 24/48 | 2.55/3.0 | 64 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 160 | 155–225 | 0–75 |
| 8224PN | 24/48 | 2.0/3.0 | 64 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 120 | – | -5–85 |
| 8124P | 16/32 | 2.45/3.0 | 64 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 125 | 120–150 | 0–75 |
| 8124PN | 16/32 | 2.0/3.0 | 64 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 100 | – | -5–85 |
| 8024P | 8/16 | 2.4/3.0 | 32 | 6 / 1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 90 | 70–100 | 0–75 |
| 8024PN | 8/16 | 2.05/3.0 | 32 | 6/1.152TB | 4800 | 96 | 80 | – | -5–85 |
In conjunction with the AMD Epyc 8004 series processors, several OEMs and partners have introduced innovative systems and solutions to maximize their capabilities:
- Dell Technologies: Dell Technologies has launched the Dell PowerEdge C6615 server, designed to deliver high performance at a low total cost of ownership (TCO) for scale-out workloads.
- Lenovo: Lenovo has unveiled its flagship edge-optimized server, the Lenovo ThinkEdge SE455 V3. This server represents a pinnacle of energy efficiency, making it ideal for next-generation AI applications at the edge.
- Supermicro: Supermicro has introduced new edge platforms that leverage the AMD Epyc 8004 series processors. These platforms are tailored to provide robust performance and energy efficiency for edge and telecommunications data centers.
In summary, AMD’s Epyc 8004 series processors offer a comprehensive solution for diverse computing needs, with a focus on energy efficiency and performance across various deployment scenarios, from the edge to traditional data centers. Multiple partners have embraced these processors to create specialized systems optimized for specific workloads and industries.
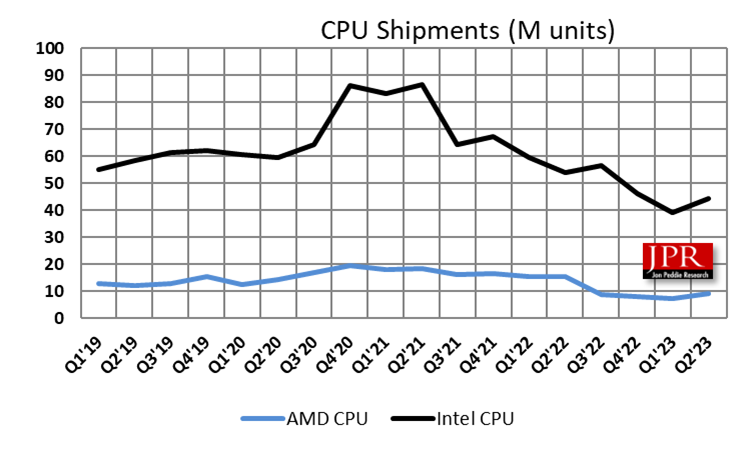
In 1973, Intel sold about 100,000 chips. Fifty years later, AMD will sell over 30 million, according to our Q2’23 Market Watch report.
AMD expects the 8004 series to further improve its market share in the desktop PC space.