Intel launched its 2nd-gen Arc B-series graphics cards, including the B580 and B570, demonstrating its commitment to the discrete GPU market. The B570 offers balanced price and performance, inheriting features like AI acceleration, XMX AI engines, and 2nd-gen XeSS upscaling. Built on Xe2 architecture with improved drivers, the B570 aims to boost performance and responsiveness. Intel claims improved performance per Xe-core and watt compared to the previous generation. Comprehensive testing, including synthetic and in-game benchmarks with ray tracing, was conducted to evaluate the B570’s performance.
In early December, Intel announced its Arc B-series graphics add-in boards, code-named Battlemage. They were the highly anticipated second generation in Intel’s Arc product line and considered a statement of commitment by the company to stay in the dGPU market.

The B580 came out in early December, and we were quite impressed by the performance of the AIB (you can see the test results conducted at our Mt. Tiburon Testing Labs here). The scaled-down B570 was released on January 16, 2025, and it is a perfect scaled-down AIB in price and performance.
The B570 carries the same feature set as its big brother, including AI acceleration and Intel Xe Matrix Extensions (XMX) AI engines. The engines power Intel’s second-generation XeSS upscaling, which includes three technologies to increase performance, visual fluidity, and responsiveness.
The architecture also features improved ray-tracing units, mesh shading performance, so-called key graphics functions, and the all-important driver stack.
XeSS 2 includes XeSS Super Resolution, XeSS Frame Generation, and Xe Low Latency. These technologies work together to increase frames per second (fps) and improve game responsiveness. Intel says the Arc B-series GPUs offer improved performance per Xe-core and performance per watt compared to the previous generation.
The individual 2nd-gen Xe-core has eight SIMD16 processors and can be set up in a variety of configurations. The SIMD’s ALUs are stacked up to form a vector engine useful for graphics and AI training.
The general specifications for the AIBs are shown in Table 1.
Intel B580 | Intel B570 | Difference 580/570 | |
Clock Speed | 2670 MHz | 2500 MHz | |
AIB price | $250 | $219 | 14% |
GDDR GB | 12 | 10 | 20% |
Xe-cores | 20 | 18 | 11% |
RT cores | 20 | 18 | 11% |
AI engines | 160 | 155 | 3% |
Mem bus bits | 192 | 160 | 20% |
Bandwidth | 456 GB/s | 380 GB/s | 20% |
Transistors | 19.6 million | 19.6 million | |
Interface | PCIe 4.0 x8 | PCIe 4.0 x8 | |
GPU TDP (W) | 190 | 150 | 27% |
Price | $249 | $219 | 14% |
Launch | 13 Dec. ’24 | 16 Jan. ’25 |
Table 1. Intel’s B-series AIB specifications. (Source: Intel)
At the MTTL, we ran a suite of tests on the B570 and then compared the results to the tests we ran on the B580, which can be found here.
We segmented the testing into synthetic benchmarks and in-game benchmarks employing ray tracing.
We used UL’s 3DMark Steel Nomad to evaluate the overall GPU’s gaming performance. This benchmark utilizes graphics technologies found in modern games, running at 4K resolution with DirectX 12 and Vulkan APIs. It features advanced graphics effects like volumetric skies, procedural grass, and volume illumination.
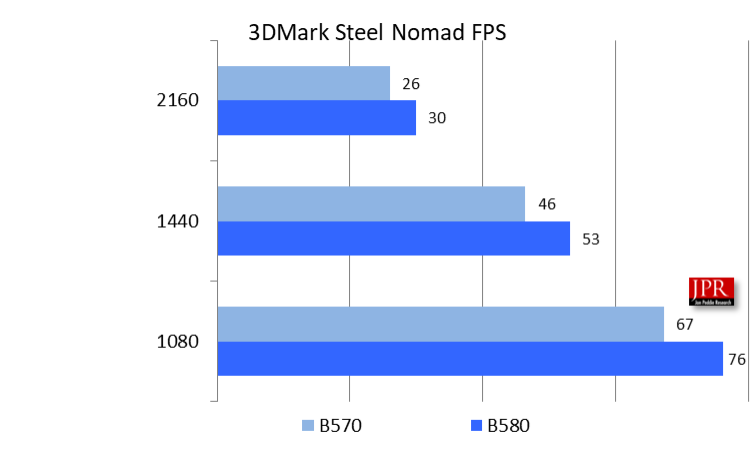
3DMark Steel Nomad is the latest benchmark from UL, building on the legacy of its predecessor, 3DMark Time Spy. Its development involved collaboration with significant industry players, including AMD, Intel, and Nvidia.
3DMark Port Royal is a real-time ray-tracing benchmark designed for gamers, utilizing DirectX ray tracing to enhance visual effects like shadows and reflections. The benchmark includes feature tests for Intel XeSS, Nvidia DLSS, and DirectX Raytracing.
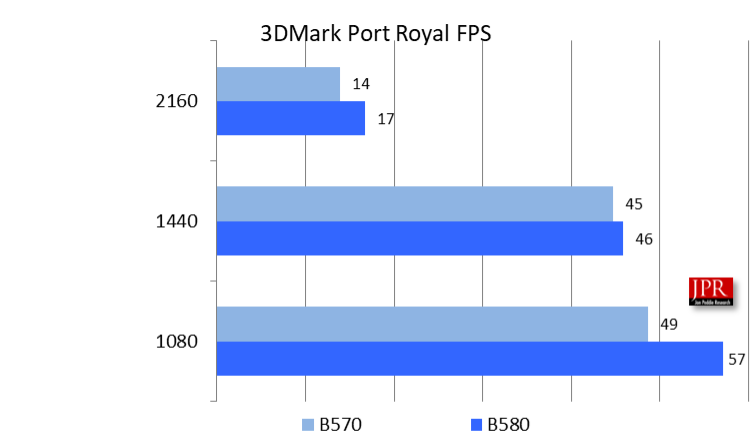
Additionally, UL offers a 3DMark DirectX Raytracing Feature test, which assesses the performance of dedicated hardware by rendering the entire scene in a single pass using ray tracing.
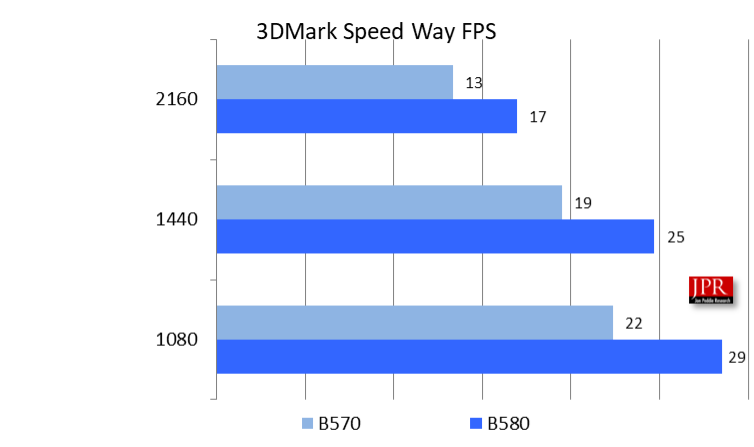
We also used 3DMark Speed Way, a UL benchmark that evaluates the performance of gaming PCs running Windows 10 or 11, with a focus on ray-tracing capabilities. This benchmark showcases features of DirectX 12 Ultimate, including mesh shaders and real-time ray-traced reflections.
UL’s 3DMark Feature test is a specialized assessment focusing on specific techniques, functions, or capabilities. The Intel XeSS Feature test demonstrates the performance impact of XeSS. Additionally, the 3DMark Intel XeSS frame inspector tool allows for a side-by-side comparison of XeSS and native-resolution rendering, enabling an interactive evaluation of image quality.
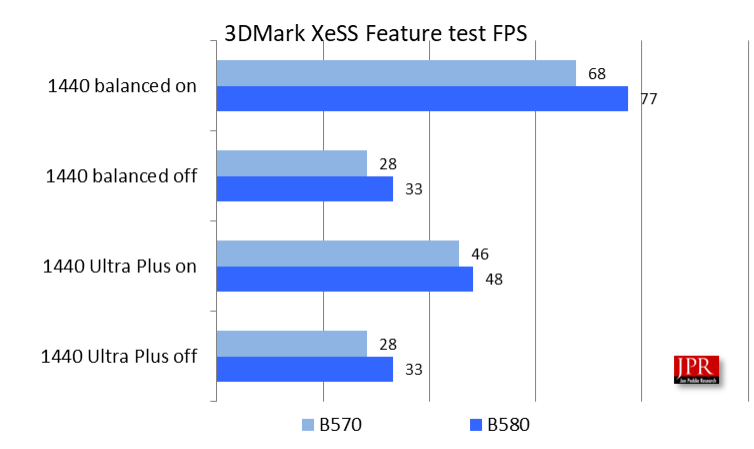
The Intel Arc B580’s performance in the UL XeSS Feature test at 1440p is shown in Figure 4. The test measures frame rate by calculating the time required to process a set number of samples for each pixel, combine the results, and display the output. The rendering resolution in this test is 2560×1440.
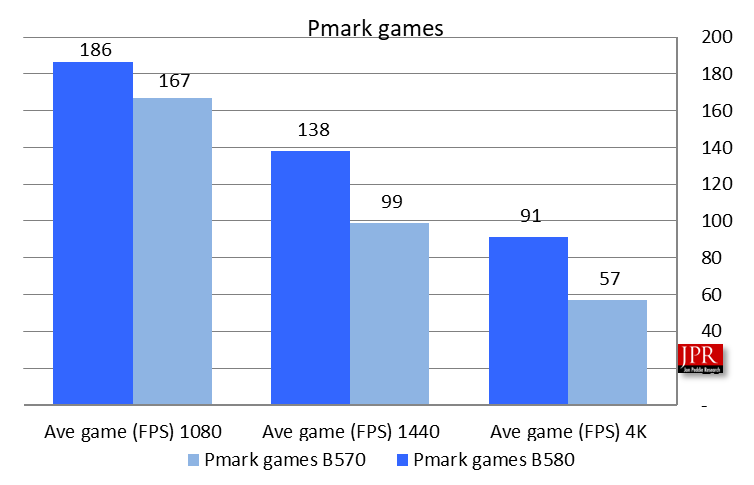
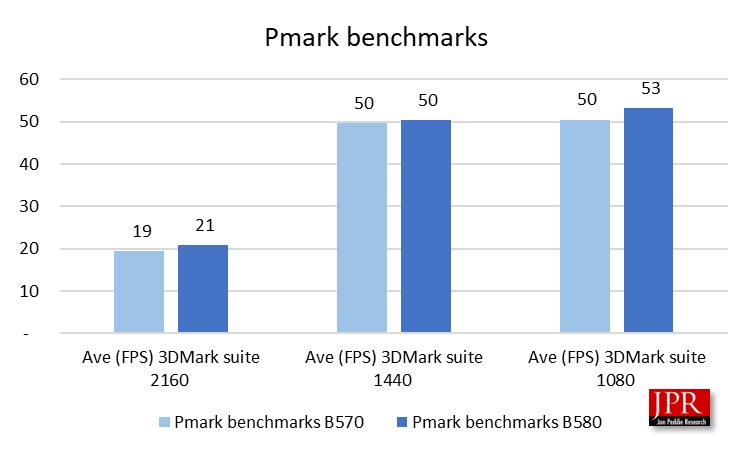
The Intel Arc B570 demonstrated strong performance in synthetic benchmark tests, as illustrated in Figure 5. Our evaluation utilized the Pmark assessment.
Blender is a very popular 3D modeling and rendering content creation software program, and it has three ray-tracing benchmarks in it. The Blender ray-tracing tests measure the performance of a computer’s graphics processing unit (GPU) in rendering 3D scenes using ray-tracing technology. Specifically, the Blender ray-tracing tests evaluate rendering speed, computational power, and memory bandwidth.
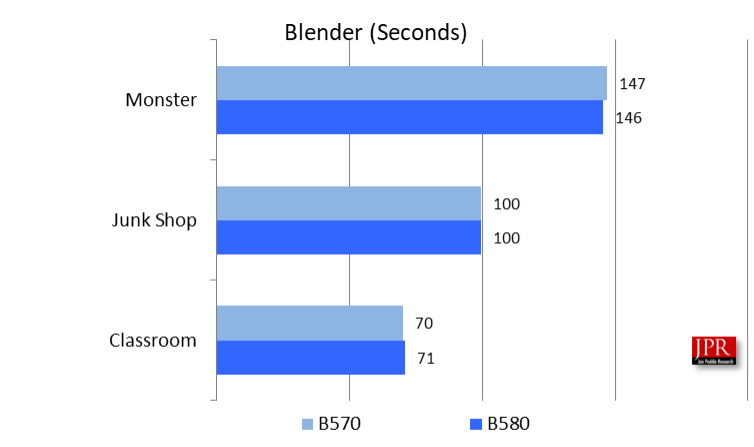
The test results are expressed in elapsed time; lower is better.
The new Intel driver showed tremendous improvement in Blender, reducing the elapsed time (with a B580) by an average of 82% in all three tests.
Game benchmark tests
In-game benchmark tests were conducted using four games with built-in benchmarking tools to ensure consistency and repeatability. Three tests were run at various resolutions and with different features enabled or disabled.
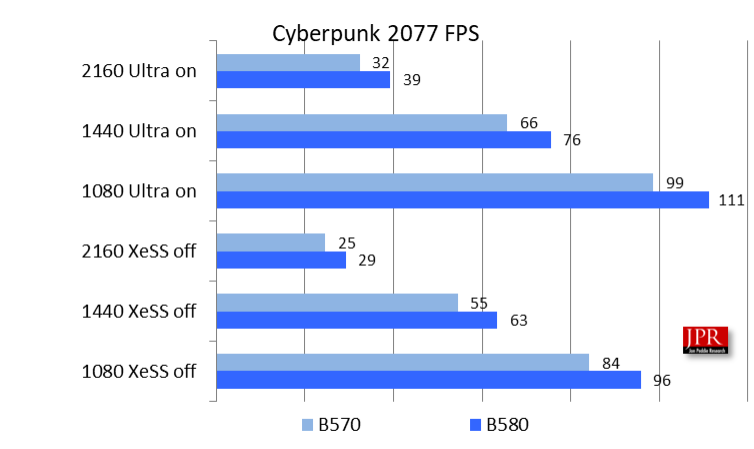
Cyberpunk 2077, developed by CD Projekt Red, was released in December 2020 as a DX12-exclusive game. The game utilizes the proprietary Red game engine and added support for Intel XeSS on April 11, 2023, as part of its 1.62 Ray Tracing: Overdrive Mode update.
When we tested the B580, there was a bug that Intel acknowledged in the 1440p test with XeSS off. Since then, Intel has issued a driver update, and it not only fixed the bug but greatly improved the overall performance—so much so we had to re-run the B580 tests.
Call of Duty: Black Ops 6 was released in October 2024 by Activision and developed by Treyarch and Raven Software. It was built on the IW 9.0 game engine, a collaborative effort between Infinity Ward, Treyarch, and Sledgehammer Games.
Figure 8 shows the benchmark results for the Intel Arc B570 versus the B580 in Call of Duty: Black Ops 6 at various resolutions.
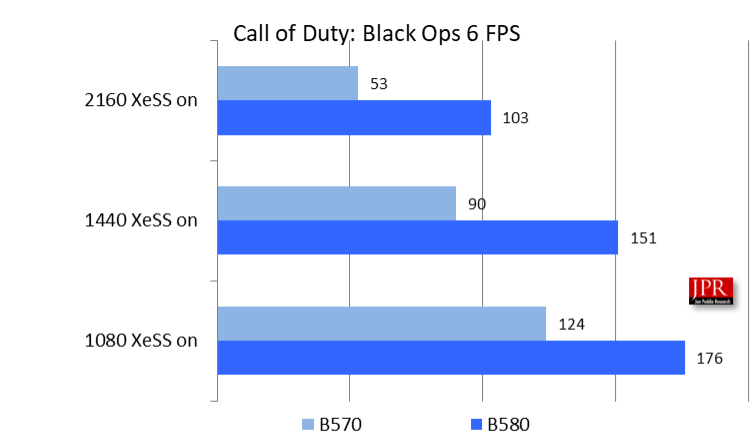
As a GPU-bound game, Call of Duty‘s performance is heavily influenced by graphics settings and resolutions. However, the CPU also plays a crucial role in handling tasks like AI, physics simulations, and game logic. Consequently, players with high-end CPUs may experience slightly improved performance when the GPU is not the limiting factor.
Despite being an older title, Shadow of the Tomb Raider, developed by Eidos-Montréal, was updated on September 28, 2022, adding support for Intel XeSS. This enhancement enabled XeSS graphics support for the game’s built-in DX12 benchmark, offering three levels of XeSS and an off option. Figure 9 displays the benchmark results for the Intel Arc B570 and B580 in Shadow of the Tomb Raider at various resolutions.
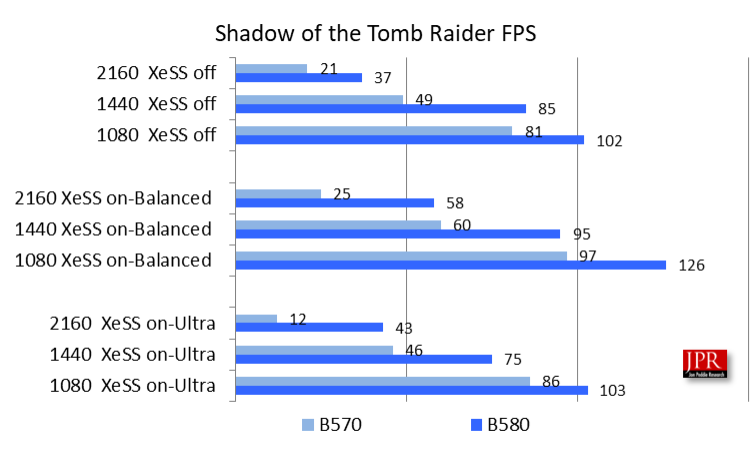
Built on the Foundation Engine developed by Crystal Dynamics, Shadow of the Tomb Raider is a visually demanding game that relies heavily on graphical fidelity, making it predominantly GPU-bound.
Chernobylite is a first-person shooter survival horror game developed by The Farm 51 in Poland. The benchmark is the most grueling one and takes 20 minutes to run. Twelve runs took over four hours. The Enhanced Edition features advanced ray-traced reflections and lighting, leveraging Unreal Engine 4 and DirectX 12. Chernobylite‘s ray-tracing effects are highly demanding, especially in Ultra settings. Figure 10 shows the benchmark results for the Intel Arc B570 and B580 in Chernobylite at various resolutions.
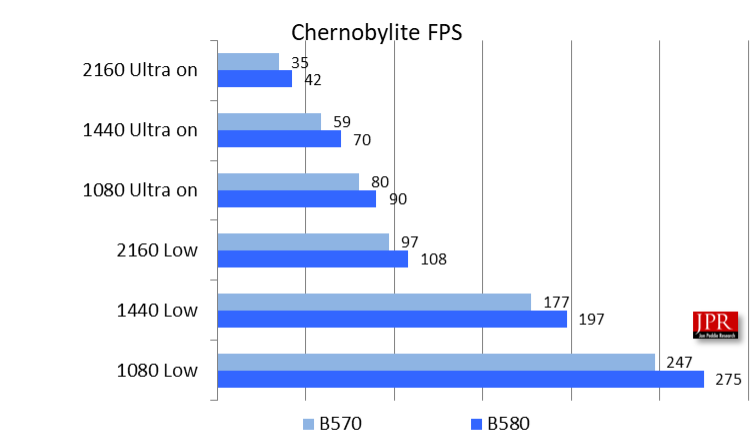
What sets Chernobylite apart is its innovative use of 3D scanning, where almost every object in the game is a digital replica of its real-world counterpart.
The Complete Edition, released in October 2022, added Intel XeSS support, and is one of the most comprehensive and time-consuming benchmarks, taking over two hours to complete six tests. As a primarily GPU-bound game, Chernobylitepushes graphics processing to its limits.
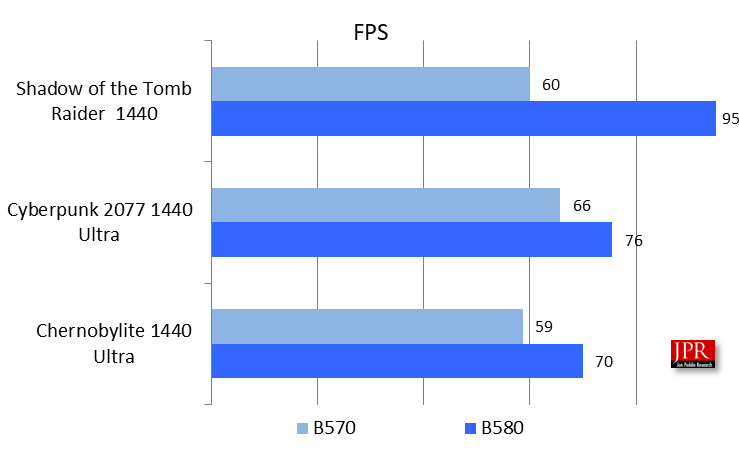
A comparison of the three leading games tested shows a relatively close match in fps performance at 1440 resolutions. Once again, that speaks to good driver design.
Pmark
The Pmark evaluation calculates a board’s overall value by considering three key factors: price, power consumption, and performance. The Intel Arc B570 scores highly due to its competitive pricing, efficient power usage, and impressive test results. However, it doesn’t beat the B580. That’s okay because it shows how good the scaling is between the two boards. That means it’s true—you get what you pay for.
Intel has two winners in the stable now, demonstrated by how quickly the B580 sold out.
In our B580 tests, we compared it to an Nvidia RTX 4060. Granted, that it is an older AIB and will be superseded by the RTX 5060 later this year, but the price and power consumption differences are notable, and value seekers will find the Intel B series a very good deal.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING? INTRODUCE US TO YOUR FRIENDS AND COLLEAGUES.