At AMD’s Tech Day in LA, the company showcased its Zen 5 Ryzen 9000 Granite Ridge CPU. Key improvements include more instructions per cycle, expanded width execution, doubled cache data bandwidth, and AI acceleration. These advancements result in an average 16% IPC uplift over Zen 4. The Zen 5 also features a new NPU, enhancing single-core machine learning and encryption capabilities. Available in Q4 2024, these CPUs offer up to 32% higher performance per watt and run at significantly lower temperatures.
At AMD’s Tech Day in LA, the company had a lot to say about its latest play—Zen 5 all the way. AMD’s Zen 5 Ryzen 9000 Granite Ridge CPU is a masterpiece of CPU design. Some of the power improvements undoubtedly stem from transitioning from the 5nm node to N4P, but AMD has also implemented additional targeted optimizations.

The key takeaway was four improvements:
- More instructions per cycle
- Dispatch and expanded width execution
- Doubled cache data bandwidth
- AI acceleration
AMD summarized it, with a relative weighting in the following diagram.
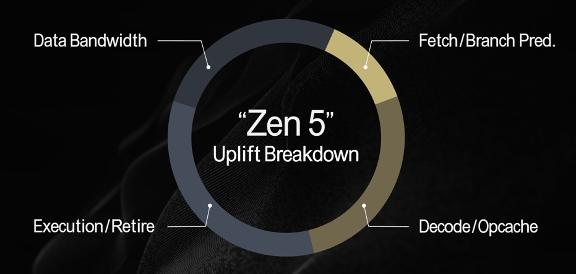
The improvements were nicely illustrated in four slides.

Zen 5’s improved branch prediction system features dual decode pipes for better branch prediction, reducing latency and increasing accuracy.

Increased dispatch and execution engines within the processor now have an eight-wide design, allowing more work per clock cycle.

The enhanced cache bandwidth of the L1 cache and floating-point unit (FPU) bandwidth has doubled, and the L2 cache is now 16-way associative.

Zen 5’s FPU supports AVX-512 instructions with a full 512-bit data path, improving throughput. As a result of those improvements and a smaller node size, when compares to the Zen 4, the company saw an average of 16% IPC uplift on tests that it ran.
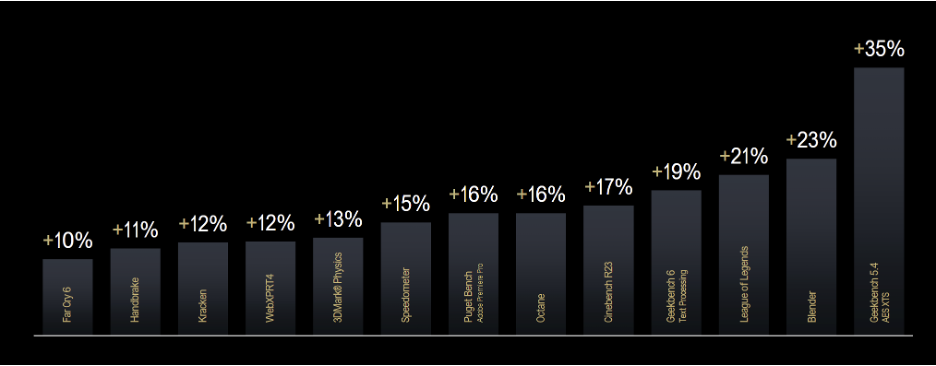
The Zen 5 also has a new NPU that the company says will give it up to 32% greater single-core machine learning capability and up to 35% greater single-core AES-XTS encryption ability.
This new and improved AI processor within the Zen 5 is called Strix Point, and the company says it will provide:
- A new foundation of performance designed for emergent workloads.
- Two unique core clusters, one optimized for peak performance and one for throughput.
- Enhanced boost sensitivity for responsiveness and efficiency.
- Intelligent scheduling on heterogeneous design.
AMD said the fifth-gen AMD CPUs will be available next month and have up to 192 cores and 384 threads. However, AMD’s 800-series motherboards may not be available, and AMD says the various motherboard vendors will release them on their own schedules.
In addition, AMD says a new confidential Al feature, based on a new trusted I/O feature, will deliver leadership in 4nm and 3nm process technologies to the data center and consumers, including mobile devices.
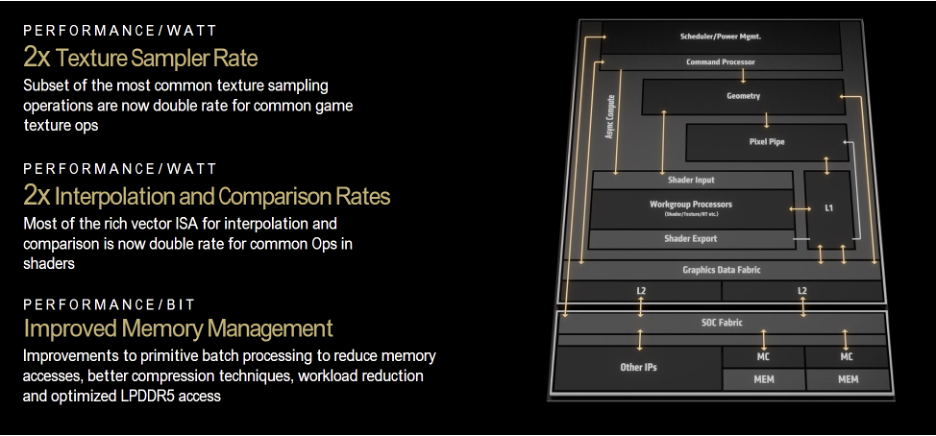
All of that results in up to 32% higher performance per watt compared to AMD’s previous Zen 4 CPU. AMD says the Ryzen 9000 runs at significantly lower temperatures than its predecessors, maintaining high-frequency residency, which leads to better effective frequency and longer boost durations.
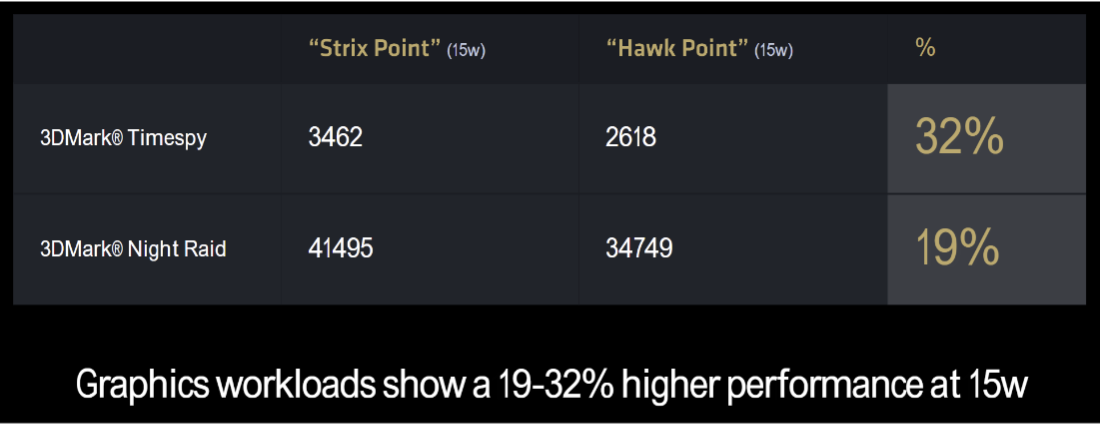
AMD is also bringing back its auto-overclocking precision boost overdrive (PBO) and claims Ryzen 9000’s lower TDP range allows more headroom for PBO gains. According to AMD, PBO engagement results in a 6% to 15% improvement in multi-threaded Cinebench performance for Ryzen 5, 7, and 9 processors, though the Ryzen 9 9950X wasn’t included in their PBO examples (likely showing only a low single-digit percentage gain).